Production planning is an essential element of the manufacturing process. It involves organizing the resources, raw materials, and labor required to produce the desired product. Various production planning methods are available, each with advantages and disadvantages. This article will explore the different types of production planning and discuss when they should be used. It will also analyze the benefits of each production planning method. Finally, this article will explore potential areas for improvement within these methods.
Production Planning Definition
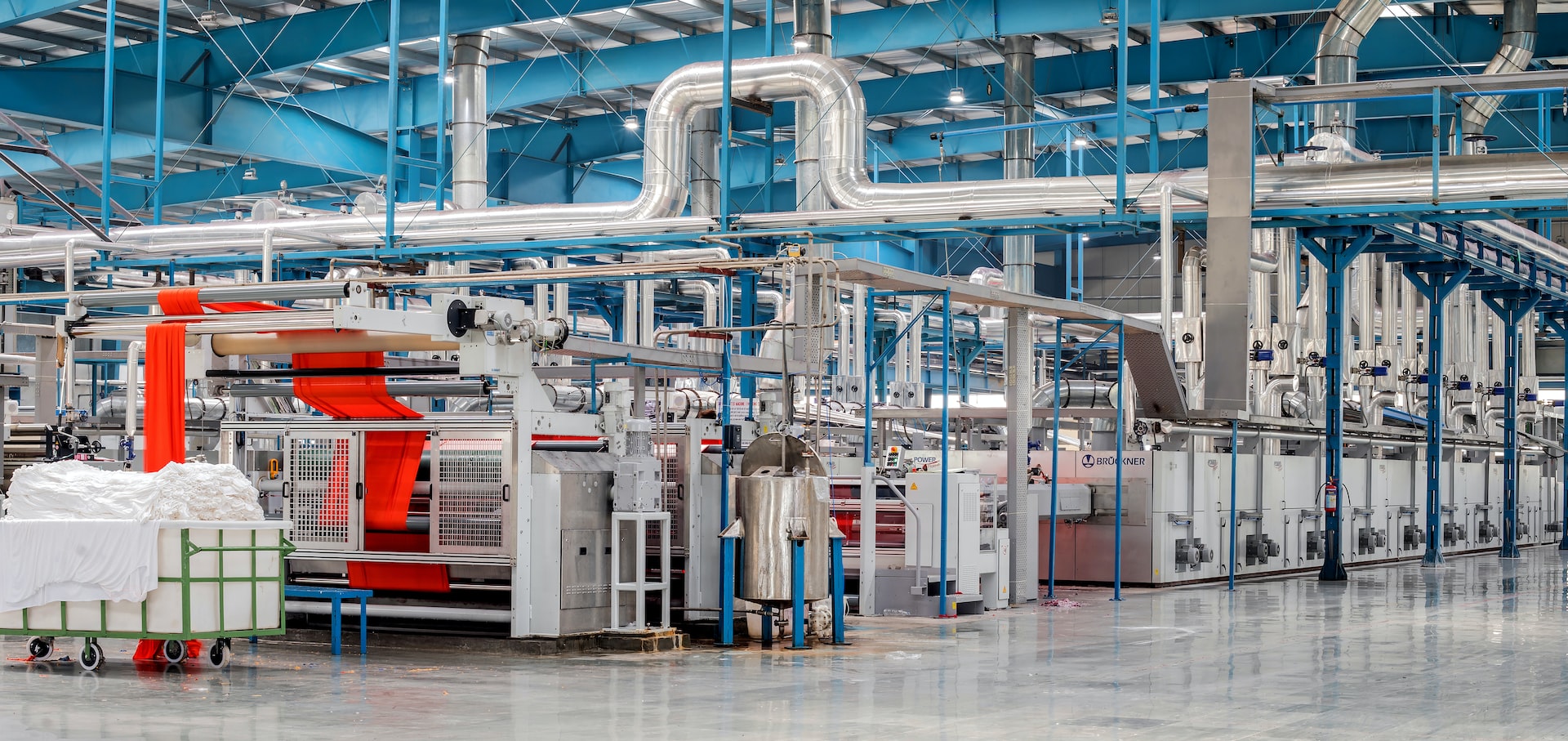
Production planning is a fundamental process in any manufacturing or production business. The organizational process determines how and when products will be produced and the quantity and quality of materials needed to accommodate customer demand. Part of this process involves ensuring that all equipment, such as sanitary equipment valves, are optimal for the production line, guaranteeing efficiency and compliance with industry standards. Essentially, it is an operational plan that determines the resources necessary to construct a product and how those resources will be used to achieve desired results.
Production planning aims to coordinate existing resources to meet customer demands while maximizing profits. Production planners must consider short-term objectives, such as meeting deadlines, and long-term objectives, such as improving efficiency and remaining competitive in their industry.
Types of Production Planning
There are several types of production planning, each suited for different needs and production environments. They also vary depending on the industry or organization. In manufacturing organizations, common types include job shop production, batch production, mass production, and continuous flow production. Job shop creates custom products according to individual customer specifications in small batches. Batch production involves making multiple items with similar specifications and storing them until they are needed. Mass Production occurs when large quantities of identical products are created quickly using specialized equipment or assembly lines. Continuous flow focuses on creating a steady stream of uniform products with only minor variations between each product produced.
One type is a job-shop production planning, which involves using specialized machines to produce custom products in small batches.
Another option is batch production planning; this method is often used when producing standardized items on a larger scale and based on customer demand.
A third approach is line flow production planning, which uses assembly lines to produce large volumes of similar products with quick turnaround times.
Finally, there’s continuous flow or repetitive production planning. This type relies heavily on automation technology, such as robots, to efficiently manufacture large quantities of identical items quickly and cheaply.
Materials Requirements Planning (MRP)
Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) is a production planning system used by manufacturing companies to manage the purchasing and scheduling materials needed for production. It analyses customer orders, inventory levels, and forecasted demand to determine what and how much material should be ordered and when it should be delivered. MRP systems are designed to minimize costs associated with maintaining too much stock or having delays in order processing due to a lack of resources. Additionally, MRP can help companies increase efficiency in their supply chain operations.
MRP systems not only plan the materials necessary for production but also track their delivery status as they move through the supply chain. This ensures that materials arrive on time which is essential for meeting customer demands. Furthermore, MRP can also be used for resource management purposes, such as tracking personnel availability or machine utilization rates throughout the production process.
Just in Time (JIT) System
The Just in Time (JIT) system is a type of production planning that efficiently uses resources and materials. JIT seeks to reduce waste, improve quality, and increase speed to meet customer demand more efficiently. It involves scheduling resources at the exact time they are needed to avoid overstocking or running out of necessary parts during production. This allows for cost reductions and improved efficiency throughout the entire process.
In contrast to traditional methods, which involve forecasting needs far in advance and producing large batches of products simultaneously, JIT requires continuous monitoring and optimization of resources used for production and understanding customer demand. The goal is to produce only what is needed when necessary, ensuring nothing goes unused or wasted while meeting deadlines.
Theory of Constraints (TOC)
Theory of Constraints (TOC) is an essential concept in production planning that optimizes resources and creates a workflow system to maximize productivity. TOC focuses on controlling and managing constraints to streamline the production process, ensuring that every step is completed efficiently and providing quick resolution when any issues arise. It helps companies identify bottlenecks, prioritize tasks, and create a plan of attack to resolve these problems so they can reach their target output.
By identifying the most critical elements in achieving goals, TOC helps businesses gain better control over their processes while improving efficiency. It also reduces risk by enabling them to anticipate problems before they become major issues, such as running out of materials or not meeting deadlines. Additionally, it ensures that products are produced on time with minimal waste and higher yield rates.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS)
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) is an integral part of production planning. It is a process that allows companies to optimize resources, such as inventory, personnel, machines, and materials, to achieve higher efficiency in manufacturing processes. APS uses advanced analytics tools to analyze data from multiple sources and provide a comprehensive view of the operational environment. This helps companies identify opportunities for improvement and develop appropriate strategies for achieving improved performance.
Using APS systems can improve quality control, reduce costs due to increased efficiencies, shorten lead times by reducing setup times and manage inventory levels more accurately. It also gives manufacturers better visibility over their supply chain operations so they can make informed decisions faster. Advanced planning and scheduling are becoming increasingly important in today’s competitive markets as it allows companies to respond quickly to customer needs while meeting cost targets and increasing profitability.
Capacity Requirement Planning (CRP)
Capacity Requirement Planning (CRP) is an essential production planning used by many manufacturing and service companies. It is a system that tries to match the capacity available with the demand for products or services. The goal of CRP is to accurately plan how much capacity will be needed over a given time to meet customer demand.
Capacity Requirement Planning uses historical sales data, current orders, and forecasted demand to calculate the total required production capacity. This information can then create an optimal production schedule that maximizes throughput, minimizes costs, and ensures customer delivery dates are met. Additionally, CRP helps identify bottlenecks within the production process so that corrective action can be taken early.
Master Production Scheduling
Master production scheduling (MPS) is a crucial element of the production planning process. It allows companies to create a detailed plan for the production process, including the timing and quantity of products that need to be produced over a specific period. MPS helps ensure that all resources are allocated appropriately and that there is enough inventory on hand to meet customer demand.
MPS considers long-term market trends and short-term customer needs when creating its schedule. The data used in MPS includes customer orders, lead times, forecasts, bills of materials, capacity requirements, supplier delivery dates, and other factors such as labor availability and machine capacity. Companies can use this information to accurately predict what they need to produce to meet their customers’ demands while optimizing their resources.
Production planning in a small manufacturing company
Production planning in small manufacturing companies is as important. The process involves setting goals, designing processes, and ensuring the resources available to deliver a product or service. It can maximize efficiency and minimize costs to ensure profitability when done correctly.
With the advance of technology and the Industry 4.0 Revolution, tools which were too expensive or too complicated became available to smaller manufacturers. Nowadays, it is enough to have a second-hand laptop computer or tablet and an Internet connection to start production planning. There is no need to invest in the sophisticated systems or planning methods mentioned above. For a small company, the best approach would be inexpensive cloud production planning software.
Thanks to such program managers and staff members can coordinate all of the necessary resources and tasks involved in the process. This includes scheduling machines, workers, materials, supplies, tools and equipment so that they are ready when needed throughout the entire process. Suppose you add to planning an effective inventory management system to avoid delays caused by waiting on materials and have all the tools needed for shop floor management.
Conclusion
Various types of production planning are utilized in businesses today because it is essential for any business that produces a physical product to stay organized and efficient. Each method has unique advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully considered when selecting a production plan for your business. With careful research and consideration, choosing the right software solution can help streamline operations and increase efficiency in any business environment.