Solar panels are highly useful but they become useless in the darkness of night. To get the lighting at night, battery storage is required which drives up the cost.
But a new invention could soon allow us to harvest energy from the cold night sky.
A new edge in renewable energy:
Raman developed a device that can harness energy even during night by channelling the day’s residual warmth into cooling air.
Raman said, “Our work highlights the many remaining opportunities for energy by taking advantage of the cold of outer space as a renewable energy resource,”
“We think this forms the basis of a complementary technology to solar. While the power output will always be substantially lower, it can operate at hours when solar cells cannot.”
Science behind:
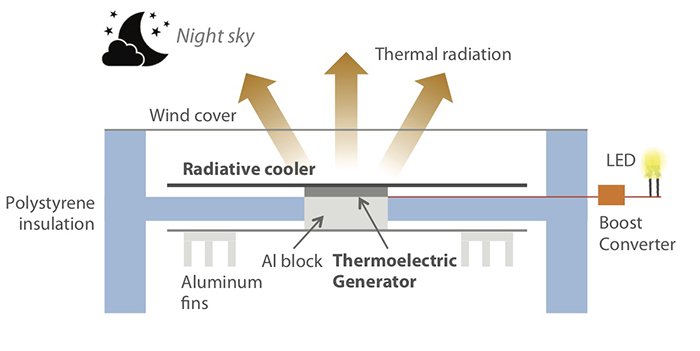
The device takes advantage of radiative cooling, the process that allows objects to release heat after the Sun sets.
Top and bottom portion of device releases heat unevenly. Top portion cools down more quickly than the bottom. This device converts the difference in heat into electricity with the help of a thermoelectric generator.
Although, it is a great innovation, but the device is not very powerful
Raman and his colleagues have tested their low-cost thermoelectric generator under a clear December sky. The device was connected to a voltage boost convertor and a white LED. Researchers measured its power output over six hours and found that it generated as much as 25 milliwatts of energy per square meter — enough to light a small LED bulb.
Though the prototype is not powerful enough but it can operate at hours when solar cells cannot. It definitely can be made more powerful with improved engineering.