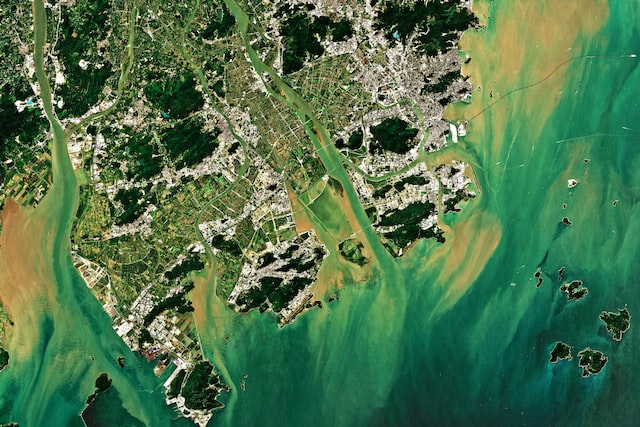
The ongoing transformations of the planet’s terrestrial surface caused by natural and human activities are known as land use and land cover changes. Precise georeferencing and regular re-acquisition of geospatial data have made geographic information systems (GIS) and remote sensing the major techniques for detecting such transformations.
Change detection with multi-temporal satellite imagery is widely used to quantify, map, and trace patterns of how an area has transformed between several dates. Updated and accurate land use/cover data gives critical input to decision-making in agriculture, forestry, urban planning, environment, and hydrology to name a few.
Detecting Changes in the Use of Land
The value of GIS-enabled change detection lies in the ability to analyze spatially and temporally changing environments around the globe. It is a comparison of two data inputs collected on different dates and covering the same area. The data for analysis can be sourced from satellites and aircraft carrying sensors that capture Earth images.
Decades’ worth of open-access satellite data has turned satellite-based change detection in GIS into the most cost-effective method to date. Just like any, it has certain limitations. To obtain accurate results, the images must have the same data source (e.g., Sentinel-2) and processing level (Level-2A, the bottom-of-atmosphere reflectance corrected orthoimage).
Types of Transformations in GIS
The change detection analysis aims at tracking four types of feature transformations.
- Location. For instance, based on InSAR and RPAS scientists pinpoint and measure glacier movement.
- Shape. With geospatial data covering a decade, scientists analyze the evolution of coral reef habitats in terms of shape and extent.
- Size. Differences in large-scale features can be easily monitored from space. To this end, change detection algorithms prove useful in urban sprawl monitoring.
- Identity. When a store becomes a house, we are talking about changes in the feature identity (in this case, the type of land use went from commercial to residential).
The Value of GIS for Business
Geospatial data in form of various images and maps has made a shift from purely scientific applications to multiple business usages. Just like scientists are designing algorithms for near to real time change detection of land cover with MODIS satellite data, businesses are launching precisely targeted marketing campaigns based on GIS-enabled user segmentation.
Brand Preferences
Brick-and-mortar stores represent location-driven business, where the address of the point of sale is a key influencing factor in the purchase decision alongside the price. With the help of GIS and spatial analytics, retailers can make use of geographic data to spot brand preferences and identify spending patterns at various scales (from district level to country level).
Customer Relationship Management
GIS data and analysis serve as an additional source of insights into what the customers want. Knowing their needs, preferences, and behaviors, businesses can make informed decisions regarding pricing, staffing, and supplies. Reliance on GIS has the potential for driving more sales and enhancing customer experience.
Logistics Optimization
GIS technology has a proven track record of aiding delivery companies with logistics. The aggregation of data from mobile devices and GPS trackers enables GIS to provide real-time tracking of assets in motion. The multitude of geospatial and other business intelligence data helps to plan more efficient and safer delivery routes to save costs and reduce delivery times.
New product development
Companies are leveraging geospatial analysis whenever they think of rolling out a new product, feature, or promotion. Knowing their customers’ habits and wants, businesses can run location-specific campaigns for new products for greater impact or offer time-specific menus in areas with high foot traffic.
Change Detection for Agriculture
The ever-growing adoption of GIS and remote sensing within precise agriculture promises to play a key role in increasing global productivity.
Companies create value for farmers by blending GIS with agri-expertise and developing solutions catering to agricultural needs. One kind of image change detection software that can radically improve farmers’ work is EOSDA LandViewer.
This online tool can easily trace changes within a field by comparing a pair of satellite images from different days. The change detection algorithms perform imagery analysis based on a default index (NDVI, NDWI, etc.) or a custom one, which makes for diverse agricultural applications. Among them are tracking changes in vegetation, land cover, crop rotation, and field state, assessment of damage, and risk prediction.
Non-Commercial Uses
Public and non-profit establishments can benefit from the existing GIS methods alongside businesses. It has become much easier due to the emergence of free tools and open-source data. Now, GIS market offers IT solutions that can be used by non-experts to let nearly everyone access the valuable insights held within geospatial data. One example of use is the monitoring of the disease spread by healthcare establishments.