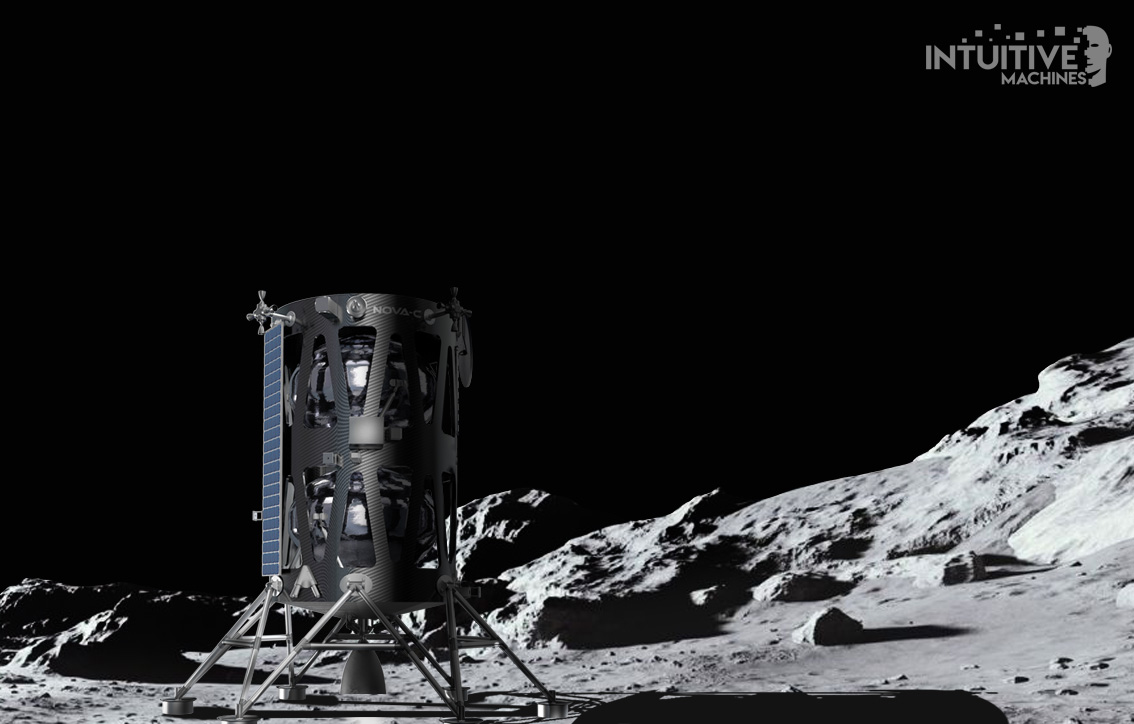
Intuitive Machines has selected SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket to launch the company’s commercial Nova-C Moon lander as early as July 2021.
After the landing failure of Israel’s Beresheet probe on the moon in April, SpaceX will become the second company to launch a private spacecraft to the Moon in 2021
A Falcon 9, which was also used in the failed Israeli landing attempt, will payload the Houston-based Intuitive Machine’s Nova-C lunar lander. If successful, this will be the first soft-landing of a private spacecraft on the Moon and will fly five NASA payloads.
Intuitive Machine’s is one of three companies awarded contracts to fly multiple missions to deliver equipment and do work for NASA on Mars surface. Intuitive Machines, which specializes in autonomous systems was the obvious choice because of its mobility through multiple relocations on the moon’s surface with the aid of autonomous systems.
The next two companies to send landers to the Moon for NASA are Orbit Beyond and Astrobotic. NASA has funded the three companies in the region of $77million for the missions.
The CEO of Intuitive Machines, Steve Altemus, had this to say: “Intuitive Machines is thrilled to sign with SpaceX to take Nova-C on its first mission to the Moon. SpaceX’s ability to make low-cost quality lunar transport is paramount to completing NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contract and Intuitive Machines becoming the first commercial company to land on the Moon.”
A statement from SpaceX president Gwynne Shotwell reiterated the following: “We’re honored that Intuitive Machines selected Falcon 9, SpaceX’s tried and true workhorse, for this pioneering mission to the Moon. Our partnership with Intuitive Machines is a great example of two private companies working together with NASA to advance space exploration.”
The liquid-methane propelled SpaceX rocket will deliver the Nova-C to the moon’s surface where it is planned to venture for 13 days before returning to earth.
This historic undertaking by SpaceX and Intuitive Machines will have a cargo of 220 lbs and it seems set to become the norm for future space explorations to Mars and beyond.