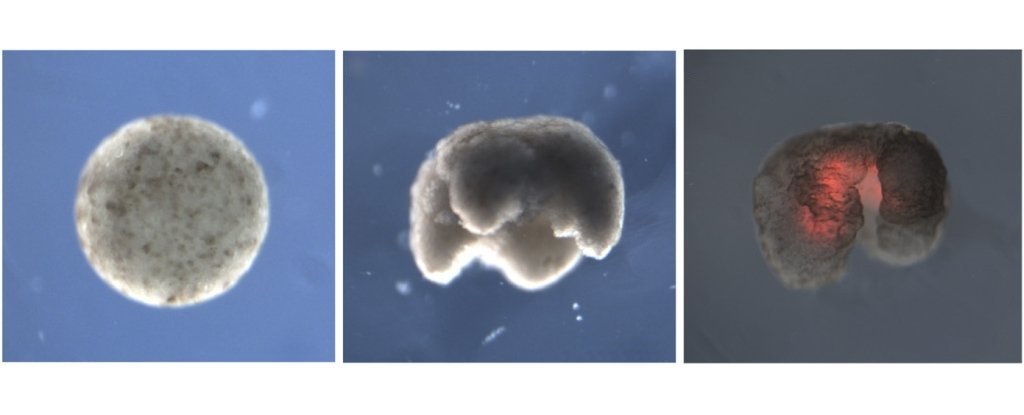
Researchers from Tufts University in the US have created living robots called xenobots. Scientists created these using embryonic stem cells from frogs.
These xenobots can move and can heal after injury. These tiny creatures were designed on a supercomputer at UVM—and then were assembled and tested. These are just a 25th of an inch (1mm).
Joshua Bongard, research co-leader said, “These are novel living machines,” “They’re neither a traditional robot nor a known species of animal. It’s a new class of artifact: a living, programmable organism.”
These can be programmed to work as required:
Scientists foresee these biological machines could be used to deliver a drug payload to a specific area in a patient or to clean up microplastics in the ocean.
Xenobots are biodegradable:
Unlike metal or plastic robots, these biological robots leave no trace behind. Professor Bongard, said, “These xenobots are fully biodegradable – when they’re done with their job after seven days, they’re just dead skin cells.”
‘We sliced the robot almost in half and it stitches itself back up and keeps going. This is something you can’t do with typical machines.’