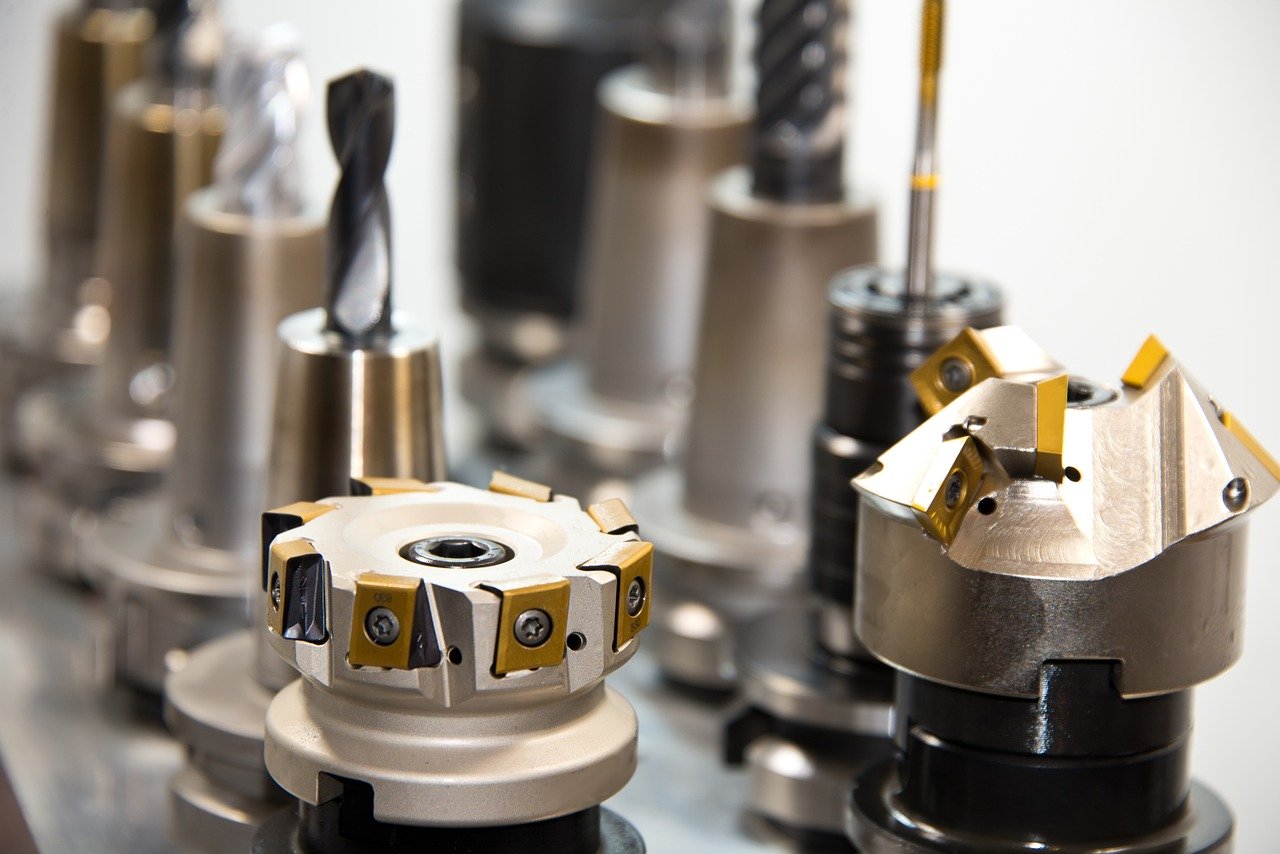
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) is the automation of machine-based instruments via the use of computers programmed to perform specific commands. Wood routing, 3D printing, laser cutting, you name it, there is a CNC machine for almost every commercially used manufacturing application and process.
Precision CNC machining works with different materials including woods, metals, foams, thermoplastics, and acrylics.
CNC systems usually vary in their composition. This is mainly because some systems tend to combine all required tools into an individual unit while other designs include individual, tool-specific units that are interconnected through external controllers. No matter the composition, all CNC systems accommodate automation of both the design and manufacturing process of your desired machined part.
Nearly all designers and users are familiar with CNC machining. Many of whom are also familiar with “precision machining.” However, those looking for services like this— specifically people considering an alternative to manual machining— probably do not know what each term indicates or, what they are actually getting out of a precision machine product.
Precision Machining Explained!
Precision machining is used to remove raw materials from a workpiece while maintaining close tolerance finishes. This helps create a perfectly finished product. In other words, it demonstrates shaping large material pieces into more specific parts. This way, they can meet the precise specifications. The process consists of cutting, turning, milling, and electrical discharge machining. It is usually performed with the help of CNC equipment.
Precision manufacturing is defined as the manufacture of individual pieces with extreme accuracy. This type of machining produces both small and large objects we use on a daily basis. Whether you’re aware of this or not, each tiny piece of a particular object generally requires some sort of machinist’s skills. Similarly, a machine or tool that is worn down typically requires machine tool calibration, grooving, or welding by an expert precision machinist.
From automobile productions to the manufacturing of aircraft parts and surgical devices, precision CNC machining is included in every industry and technology you can think of. So, essentially, if an item you’re familiar with has parts in it, chances are it probably went through some sort of precision machining.
Normally, precision CNC machining is specified by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to transform certain materials. Precision machinists, as briefly explained above, take raw material—usually metal—and then shave it down to the desired shape.
Precision CNC machining utilizes Computer Aided Design (CAD) or Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM). This offers the most accurate measuring/cutting to the said specifications. The machining process is widely used to create a variety of objects, such as:
- Surgical instruments,
- Wind and solar components,
- Aerospace components
Although drill lathes and presses are utilized in combination, the use of high-speed robotics isn’t uncommon with the latest technology in precision machining.
Machining — A Brief History

Photo by Jordan Benton from Pexels
Believe it or not, machining actually dates back to 700 BC. However, the sad thing about it is that there weren’t any buttons you could push then. Instead, a manual lathe was the only instrument you could use.
In the late 1700s AD, steam power made things a lot easier. By incorporating steam, machining turned automated and so began the Industrial Revolution in all its glory. The production of machine tools on large scales upgraded steel-creating processes everywhere, aside from a range of other innovations.
Modern CNC machining has since gone from utilizing punch cards in the late 40s to genuine computer technology for programming we use today.
What Is It Used For?
It’s crucial to understand why precision CNC machining is utilized for a specific part. That said, precision machining is used to perform a number of tasks, such as:
- Creating precise movement
- Reducing the startup cost
- Providing an extended life span for the part (also, higher precision indicates less damage in day-to-day use)
- Increased interchangeability
- Increased safety
- Enabling better miniaturization of parts
- Reduction in the dispersal of the part’s function
- Improvement in the overall quality control
Due to the accuracy and precision required for certain parts, it’s essential to maintain a high accuracy level across the entire range of part sizes and in order to be able to accomplish this in the long run. That’s where precision CNC machining stands out compared to other technologies.
The Materials Used in Precision CNC Machining
We all know the use of stainless steel in high-quality machining. Its properties have made it one of the most widely preferred materials in all types of machining.
So, does precision machining make use of stainless steel? Of course, yes! However, it isn’t the only material used. Aluminum, plastic, ceramic, bronze, brass, copper, composites, graphite, titanium, Kovar, tungsten, Inconel, Ni 200, and Nitronic are just some of the materials the precision CNC machining industry works with.
The Tools Used in Precision CNC Machining
Well, it depends on the material being employed; for most materials, milling machines, saws, lathes, grinders, 3-axis, and 5-axis CNC machines are used. These are basically CNC controlled tools operated by experts and qualified operators. In a handful of cases, photochemical processes and robotics may be used to produce the high-tolerance parts.
Every machine and tool has its own sets of unique capabilities. Also, the material, size, and complexity of the final part, the finish, etc. will impact the choice of tool employed.
The 5 Most Notable Advantages of Precision CNC Machining

Image by Michal Jarmoluk from Pixabay
Operational Efficiency
As you can tell by now, the whole precision machining process focuses on computer-controlled tools and machines capable of operating automatically at great speeds without any manual input. This means a lot for manufacturers as they can now rely on less workforce for processing the parts.
The reduction in manufacturing costs and enhancements in the quality of the product will improve the operational effectiveness of the factory floor. That said, skilled labor is still required to operate more advanced systems and machines.
Little to No Risk
Errors, be it mechanical or human-made, can severely hinder the production process, thereby increasing the manufacturing cost. However, with the help of intelligent machines, it’s possible to reduce errors from specific processes. Computerized tools do not make many errors as they are programmed to execute a specified number of actions.
Incredible Speed
Precision CNC machining is built to deal with the equipment utilizing computer-animated drawings. This helps to interpret blueprints and function accordingly. These tools can precisely outperform human labor when it comes to speed and accuracy.
Moreover, machines don’t require any sleep, so they are able to run for longer periods and help produce products at large quantities while maintaining consistent quality.
Low Manufacturing Costs
Precision machines are mostly used to produce precision components. The all-inclusive nature of this process leads to less labor, reduced waste material, and little to no error. Low production cost is one of the reasons the manufacturing industry today relies upon computers to run their daily operations.
Rapid Production
You know how quickly and efficiently automated manufacturing systems can perform the same tasks over and over with better accuracy. This is why humans can never beat precision engineering machines in terms of accuracy and speed. Reduced turnaround hours will help businesses meet market expectations.
If you’re looking to gain sustainable growth, there are no better options. Precision CNC machining can be a total gamechanger. It can allow you to reshape your product design and keep the tight tolerances as per your industry demand.