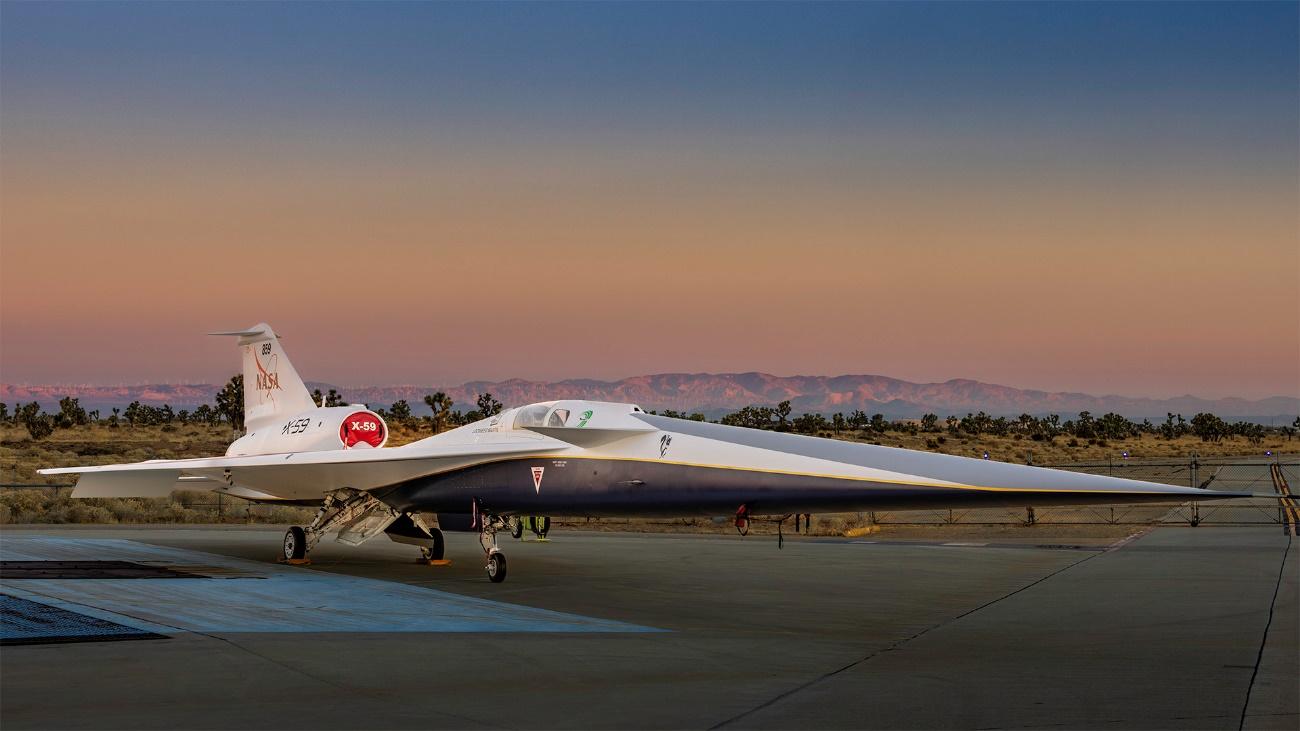
The quiet supersonic aircraft X-59 was formally revealed by NASA and Lockheed Martin. The X-59 is an experiment for data collection that will be used by NASA to revolutionize air travel by enabling commercial aircraft to reach speeds greater than the speed of sound. The ceremony took place at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works at the Palmdale, California facility.
As said by Pam Melroy, NASA Deputy Administrator, “This is a major accomplishment made possible only through the hard work and ingenuity from NASA and the entire X-59 team,”, adding that “In just a few short years we’ve gone from an ambitious concept to reality. NASA’s X-59 will help change the way we travel, bringing us closer together in much less time.”
This aircraft is part of NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to help regulators reconsider the ban on commercial supersonic flights over land. As the aircraft will be able to fly at speeds of 1.4 times the speed of sound, such flights will cause a sonic boom. That is the reason why countries, including the U.S., have banned such flights for 50 years. However, with its design, shape, and technology, the X-59 will be able to produce much quieter sonic booms.
Bob Pearce, associate administrator for aeronautics research at NASA Headquarters in Washington, sad that “It’s thrilling to consider the level of ambition behind Quesst and its potential benefits,”, adding that “NASA will share the data and technology we generate from this one-of-a-kind mission with regulators and with industry. By demonstrating the possibility of quiet commercial supersonic travel over land, we seek to open new commercial markets for U.S. companies and benefit travelers around the world.”
As a further step, the team will start preparation for the first flight, which will take place later this year. Then, the data will be provided to the Federal Aviation Administration as well as international regulators.