Overcoming Recycling Challenges in 3D Printing
As the popularity of 3D printing continues to rise, there is a growing concern about the recyclability of the plastic materials used in this process. Despite the development of sustainable alternatives, their widespread adoption is hindered by the complex adjustments required in 3D printer settings for each material. Typically, initiating printing with a new material involves meticulously configuring up to 100 parameters within the controlling software, which governs the crucial extrusion process for fabricating objects.
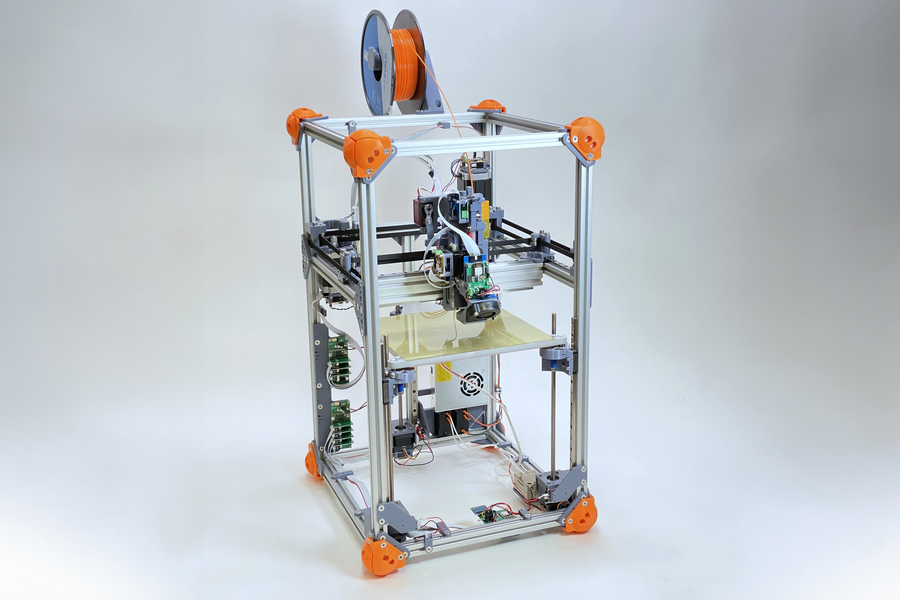
Now, researchers at MIT have unveiled a groundbreaking new printer capable of handling sustainable materials. This development holds immense potential for the future of 3D printing, pushing the industry towards a more eco-friendly approach.
Traditionally, 3D printers have been limited by the specific properties of the filament they use. This often meant excluding sustainable options like recycled materials due to inconsistencies or printing difficulties. However, MIT’s innovative printer breaks this barrier. It boasts the remarkable ability to analyze unfamiliar materials on the fly and adjust its printing process accordingly.
Expanding Horizons: 3D Printing with Recyclable Materials
This adaptability opens a new chapter in 3D printing, allowing for the utilization of a wider range of renewable or recyclable materials, significantly reducing the environmental impact of the printing process. Imagine printing objects with bioplastics derived from plants or even recycled plastic waste! The possibilities for sustainable creation are vast.
Eco-Friendly Applications of MIT’s Technology
The implications of this technology extend far beyond just eco-friendly trinkets. It could pave the way for 3D printed products with unique properties derived from these new materials. We might see advancements in areas like bioprinting for medical applications or the creation of custom building materials with superior sustainability profiles.
This breakthrough from MIT represents a significant leap towards a more sustainable future for 3D printing. By unlocking the potential of previously unusable eco-friendly materials, this technology has the power to transform the industry and contribute to a greener world.