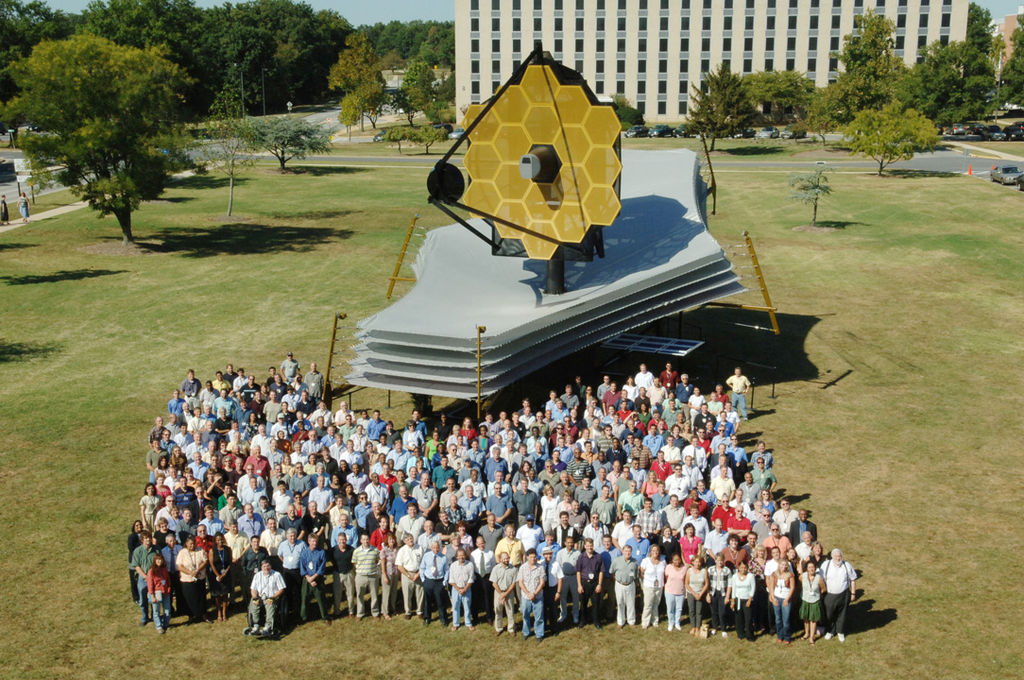
NASA’s upcoming James Webb Space Telescope (also known as Webb or JWST) is planned to be the successor to the nearly three-decade-old Hubble Space Telescope.
This space telescope is being developed in collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Webb is now one step closer to its planned liftoff on March 30, 2021
NASA originally planned to send the telescope to space way back in 2007, but the project was delayed by more than a decade due to various setbacks and human errors.
Last month, the James Webb Space Telescope’s spacecraft cleared a critical testing milestone by surviving extreme climate fluctuations from a glacial minus 235 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 148 degrees Celsius) to a sweltering 215 degrees Fahrenheit (102 degrees Celsius)
It will be the biggest, most powerful telescope ever to be put in space
The infrared Webb telescope weighs 6 metric tons and will orbit 940,000 miles (1.5 million km) away from Earth. It will be able to see further into space providing more powerful unobstructed views of the heavens than its predecessors
“Webb will solve mysteries in our Solar System, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our Universe and our place in it,” according to NASA.