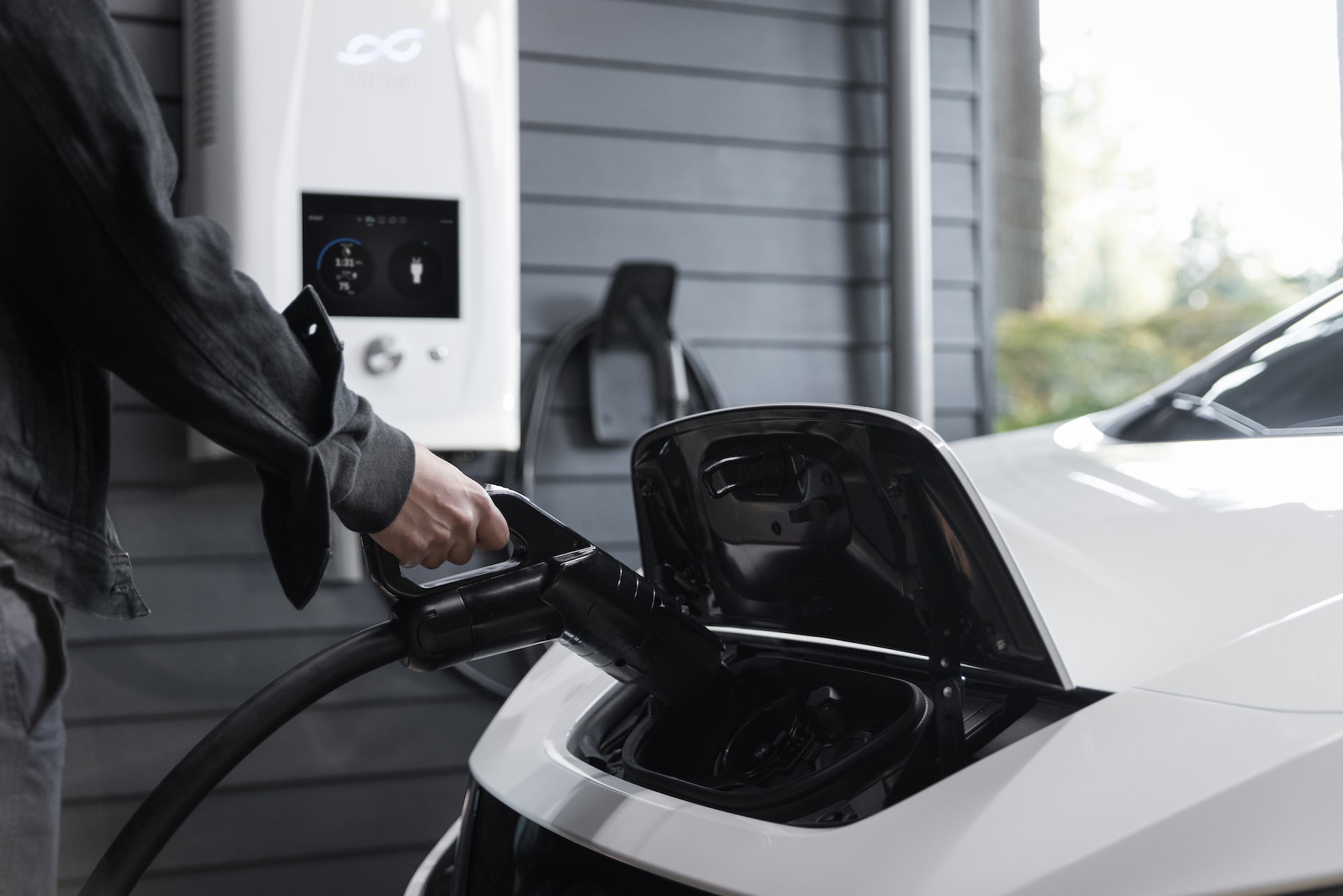
When charging your electric vehicle (EV), you may be wondering which location is best – a home or a public charging station. Well, look no further, because this article will give you a low-down on the differences between each of them, so you can decide which you prefer.
On the whole, there is no bad option. Both do a great job of charging your EV with efficiency and conveniency!
Before you think about charging, you need to make sure you find the best car insurance. This will mean you are covered if anything happens to your EV. But first, we’ll be discussing home charging points, so read on to find out more…
Home Charging Stations
What more could you want than having a charging point on your doorstep? Most people who use home chargers tend to leave their car plugged in overnight, so they can wake up to a fully-charged vehicle for the morning. This effectively means no hassle, no waiting around, and the car is being recharged in the privacy of your own property.
In the long-term, having a home charger is the cheapest option for your EV. Driving electric is cheaper than running on gas, as gas prices (at the time of writing) average around $3.50 a gallon. In order to keep costs down further, most people install an EV charging station at home.
In addition to this, having a charging port at home means you don’t have to worry about waiting in line to charge your car at a public station. Your home charger will come with a Level 1 or Level 2 charging system.
Level 1: Uses a standard household outlet (120-volt connection)
Level 2: Uses a higher volt connection (240-volts) and charges a lot faster than a level 1 outlet.
Both types of charger work effectively, and provide a reliable source of power for your EV. As an added bonus, when selling your property, if you have a built in EV charging station, it may even increase the overall value of your home.
Public Charging Stations
Now to find out more about the other EV power option – public charging stations.
These points are typically seen in gas stations or shopping malls, offering a number of chargers for EVs. They can be free, pay-as-you-go, or even subscription-based, with prices set by networks or property owners.
Some automakers, such as Hyundai, Nissan and Tesla may provide complimentary public charging at certain charging points, but it depends where you are in the state.
For example, drivers in California can pay around 30 cents per kWh to charge on Level 2, and 40 cents per kWh for DC fast charging.
DC Fast Charging: Can be found in public charging locations and are quicker than a level 1 or 2 outlet. These stations are ideal if you require a boost of power quickly.
A benefit of using public stations is that you don’t have to pay for the installation of an at-home charger. For those who want to charge as-you-go, this is a great method.
Using public charging stations allows you to be more flexible with your journey; simply pull up to a gas station, charge, and carry on driving – it’s as simple as that!
We hope this article has helped you to grasp an understanding of both EV charging options and their benefits. Which leaves the question: which will you be choosing to car your vehicle?