Superhuman Abilities Through “Evolutionary Computation”
Bionics researchers trace the baseline for their discipline to Leonardo da Vinci and his ingenious inventions which used keen observations of biological systems to design mechanical systems to emulate nature and benefit humans. The term “bionic” was coined by Jack E Steel in 1958, and is derived from the technical term “bion” meaning “unit of life” and the suffix “-ic” meaning “in the manner of” or “life like”.
More recently, the idea of “bionic humans.” was popularized in the TV series “The $6 Million Man” about Col. Steve Austin whose bionic eyes with zoom lenses and night vision, combined with bionic arms and legs made him capable of cheetah-like speed, bulldozer-like strength and a force for good in a troubled world. Now scientists are hard at work advancing “evolutionary computation,” an iterative process of programming which continually optimizes and advances human capabilities and is modeled on natural evolution.
Cybernetics & Bionics
Cybernetics is a multidisciplinary exploration of mechanical, physical, biological, cognitive and social systems while bionics is the machinery, such as small motors and actuators that are the hardware of cybernetics. The general goal of bionics is to augment human abilities, including strength, endurance and mobility and includes attempts to enhance or replace eyes, ears, noses, touch and taste. The discipline goes so far as to integrate bionic machinery with the bloodstream and nerve endings so as to make the bionic replacement as good as or better than the original, possibly increasing functionality and performance beyond normal capacity while being more durable.
Copying, Imitating & Enhancing Human & Animal Functions
Today, bionics includes cochlear implants, exoskeletons, eyes, fingers, hands and even organs. The idea is to study biological systems and organisms and find engineering solutions to impairments experienced whether due to congenital defects, injury or disease. Bionics has come so far that researchers believe in the near future the processing of bionic parts will be operated using brain or body implants as is already the case with cochlear implants.
From Body Part Healing To Life Extension
Researchers anticipate that bionics will be used to replace diseased or aged organs thereby increasing lifespans. One of the main goals is to make bionics of all types less invasive and cumbersome and with new materials and designs there is constant improvement. Professor William Craelius of Rutgers school of Engineering studies how bionics can restore mobility to people with impaired limbs using prostheses. Craelius’s research includes work with patients paralyzed due to stroke, brain injury, and cerebral palsy and the development of connections between nerves and bionic devices.
Part Human, Part Machine
Bionics, also called biomimicry, biomimetics, biomimetrics, and biognosis, is being touted as creative engineering technology that can restore almost any lost function. According to Craelius, scientists see the day when human flesh will be removed in favor of high-tech machinery, giving way to “body modification” that will be more complex and far-reaching than simple nose rings and facelifts.
Once human brains are able to manage bionic parts and hearts and lungs no longer need to power as much of the body, humans will enjoy increased fitness and stamina and will have an incentive to replace underperforming body parts. There are already artificial neurons, neural networks and the new field of “swarm intelligence”. In the interim, “strap on robots” such as exoskeletons or wearable robots will enhance strength, mobility and endurance for the disabled and fit alike.
The Downside
Not so fast warn some bionic researchers: bionics do not function well in temperatures below 32°F ( 0°C) and some give off radiation that can be detected using a Geiger counter. Doctors are already able to attach bionic limbs and operate them using surviving sensory nerves that transmit temperature, pressure and vibration. Here are some of the leading bionic authorities, projects and products today:
- The American Board for Certification (ABC) and the American Academy of Orthotics and Prosthetics (AAOP) certify bionic products and our clearinghouses for information
- Advanced Bionics – producer of the Aqua Case a leading cochlear implant product
- Cochlear Implant Online-a source for implants of all shapes, sizes and designs
- Ekso Bionic Holdings, Inc. – designer and developer of robotic exoskeletons that supplies bionic suits to 22 rehab centers in the US, eight in Europe and one in South Africa
- Cyberhand Team – creator of Longitudinal Interfascicular Electrodes (LIFEs) That connect a hand to the nervous system
- Experimental Biology Symposium – A regular symposium on bionics
- Phonak – a company that works with Advanced Bionics on hearing solutions
- Berklee Bionics – creator of the Exoskeleton Lower Extremity Gate System (eLEGS) that allows paraplegics to stand and walk with crutches or a walker. Also created the Human Universal Load Carrier (HULC) to carry heavier loads.
- Touch Bionics – creator of the world’s leading prosthetic technologies, especially upper limb issues
- Yanke Bionics – a leading provider of orthotic and prosthetic bionic devices and creator of the FastSCAN Scorpion System, a leading computer imaging and fabrication generator
- Artificial Muscle Project – MIT project to create artificial muscles with applications to robots and possibly bionics
Related articles on IndustryTap:
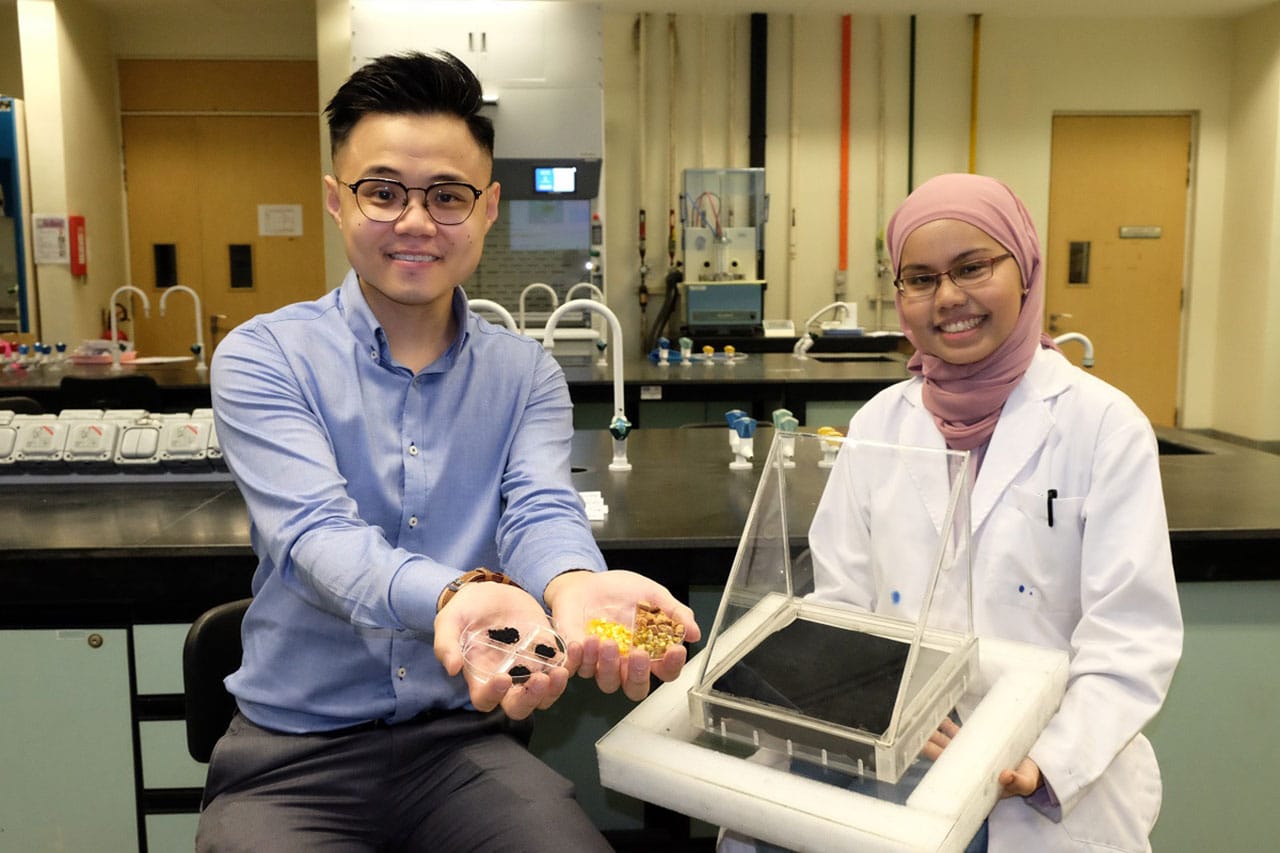
- Solar Cell Research “Births” New Field Of Nanobionics
- Using Bionics To Transcend Disabilities, Augment Human Capabilities: The Revolution Is Upon Us
- Building Complex Nanorobots Out Of DNA
References and related content: