Hydrogen-based energy is a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels due to its high energy content and environmental benefits. However, one of the challenges associated with hydrogen is its storage. Hydrogen is a lightweight and highly flammable gas, which makes it difficult to store and transport safely.
Safe storage and transportation of highly combustible hydrogen are essential for society’s shift from carbon-based to hydrogen-based energy.
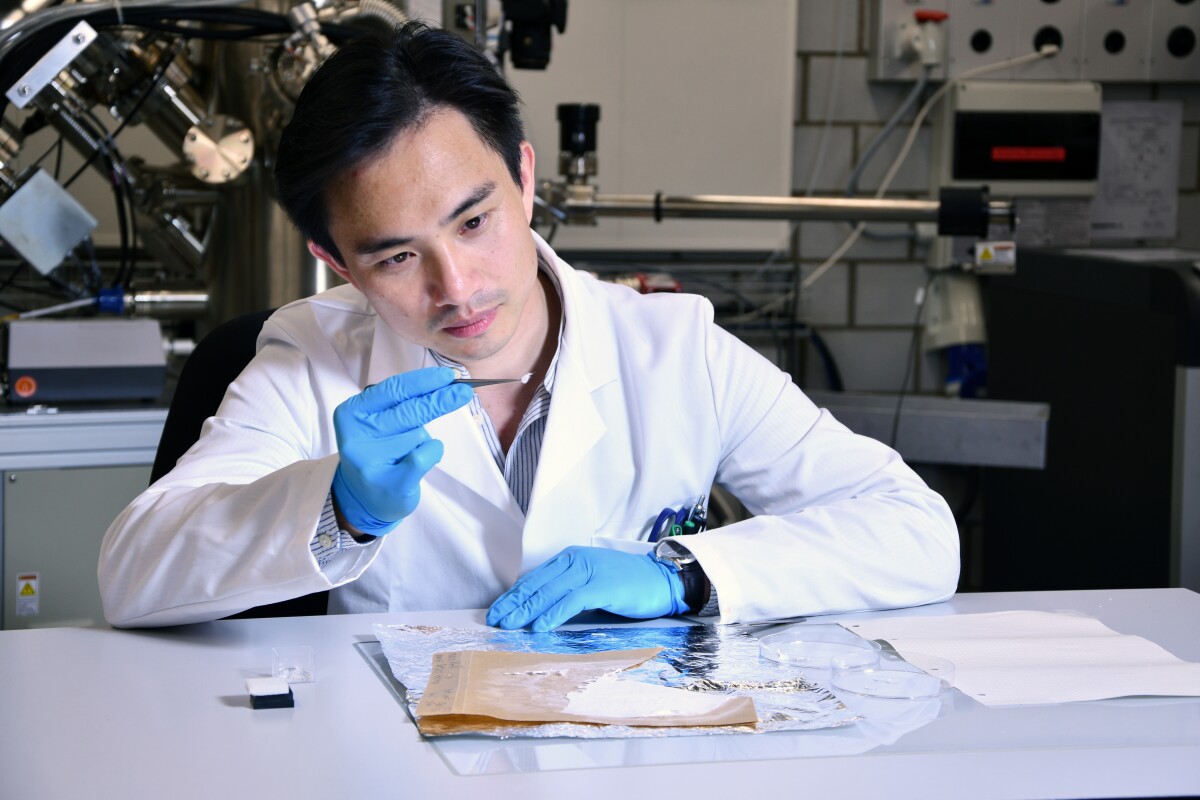
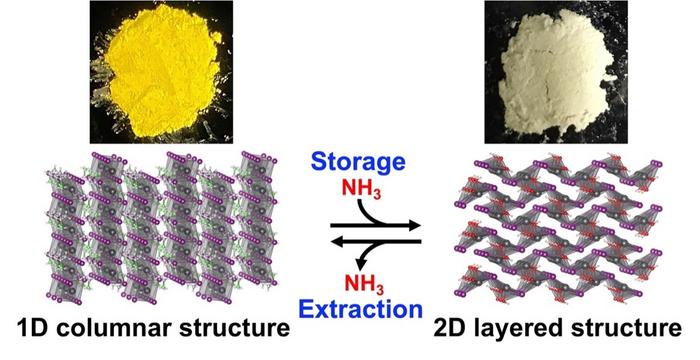
Scientists from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) have made a significant breakthrough in hydrogen storage. They have discovered a compound that revolutionizes the storage and retrieval of hydrogen by utilizing a chemical reaction.
This ground-breaking method provides a safe, simple, and cost-effective approach to storing ammonia, which serves as a crucial carrier for hydrogen.
Researchers discovered that perovskites, known for their ability to enhance energy conversion efficiencies in solar panels, can also serve as an exceptional medium for storing and retrieving ammonia.
This finding opens up new possibilities for utilizing perovskite materials in the efficient storage of hydrogen.
Ammonia is a highly corrosive gas, but perovskite enables safe storage without specialized equipment. Retrieval is simple: heating ethyl ammonium lead iodide under vacuum at 122°F (50°C) releases ammonia gas. In contrast, ammonia stored in porous compounds requires temperatures of around 302°F (150°C) for recovery.