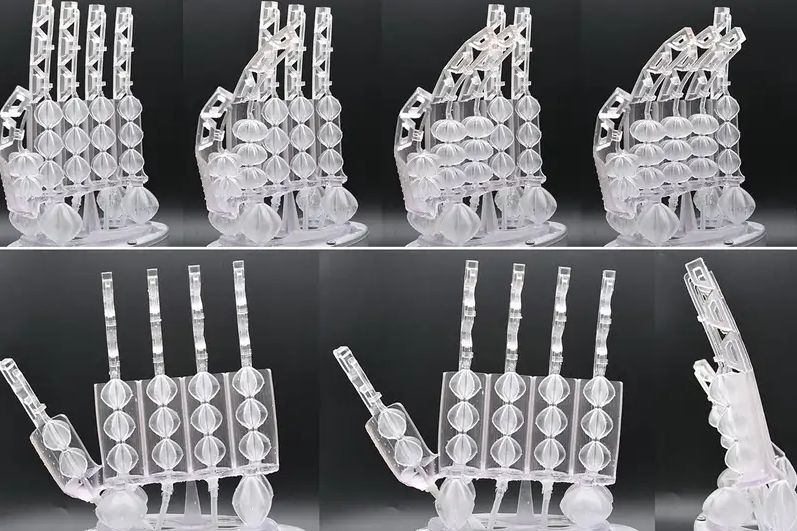
Researchers from the Italian Institute of Technology have developed a robotic hand with human-like efficiency. This robotic hand can stretch, contract, and could also grip objects with human-like efficiency.
Researchers have developed a new class of high-strength artificial muscles in a way that has never been done before. These artificial muscles are known as actuators.
Scientists foresee this development could enhance the development of 3D- functional devices such as artificial body parts.
Tiny actuators can lift up to 1,000 times their own weight
These are powered by a series of GeometRy-based Actuators that Contract and Elongate (GRACE). GRACE is driven by the influence of gas, or compressed air. In this study, researchers combined 18 of these novel actuators, for creating an 8-gram (0.01 pounds) robot hand. They found it was able to lift up 8 kilograms (17 pounds).
According to Jonathan Aitken at the University of Sheffield in the UK, “The GRACE’s design is interesting and novel, providing simple antagonistic operation by design.”
Actuators are 3D printed from a resin membrane
The choice of flexible resin for the actuator gives a greater range of movement than the stiffer resins used up until now. But according to Aitken, this flexible resin could further be improved.
He claims, “The range of capabilities of devices printed using them will increase the more novel resins that can be developed with excellent tensile properties,”