Power plants fuel our homes by generating electricity in real time but when we don’t need the electricity; the excess energy generally goes waste.
Energy storage is a big challenge. Though the plants running on fossil fuels can be turned on as per demand, wind turbines or solar plants produce power only when the wind is blowing or sun is shining.
MIT engineers have found a new solution to store renewable energy
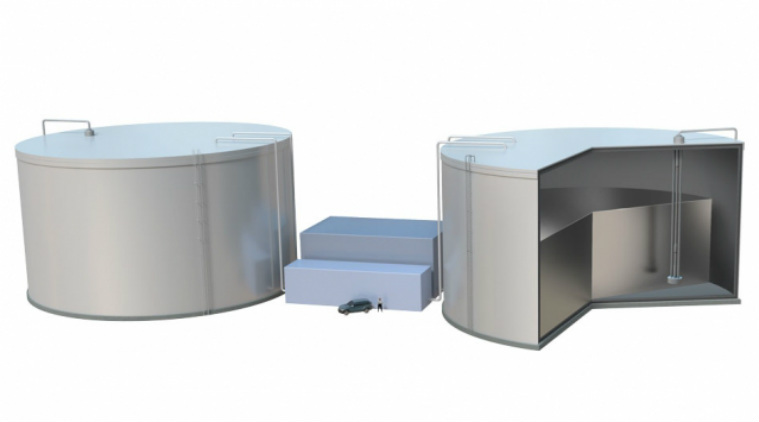
Engineers at MIT have developed a ‘sun in a box’. The box is full of white-hot molten silicon. Silicon,which is available abundantly on the Earth, can operate safely at a much higher range.
The heat generated by excess electricity from solar or wind power is stored in the box or tanks of white-hot molten silicon. The heat is converted back into electricity when it is needed.Researchers already have developed a pump that holds the Guinness World Record for the highest heat tolerance which is the key to the overall concept.
Researchers claim that sun in a box is far more affordable than lithium-ion batteries, which is an expensive method to store renewable energy.
According to the researchers, a scaled-up version of the ‘sun in a box’ system using 10-meter tanks would allow a small city of 100,000 homes to be powered by renewable energy.